Encryption Feature For Web-Based Version of Outlook
Encryption Feature from Web Based Version of Outlook
Encryption is a way of protecting private information and passwords from being stolen or compromised when information is sent between a browser and a server. This is especially important with persons connecting from remote offices. Encryption is defined as the conversion of data from a readable format into an encoded format It is the simplest way to ensure that information is not stolen and used for malicious purposes. Encryption converts plain text into what is known as incomprehensible ciphertext. Encrypted data can only be read and processed after it has been decrypted. It is strongly recommended that users ensure that their data is encrypted while in storage on the cloud.
Both Outlook and Outlook Web App support the S/MIME encryption control and should be used to send and receive encrypted or digitally signed messages.
The S/MIME control is necessary to verify the signatures of digitally signed messages, but a certificate is not. If you receive a message that's been encrypted or digitally signed and the S/MIME control is not installed, you'll see a warning in the message header notifying you that the S/MIME control isn't available. The message will direct you to the S/MIME options page where you can install this control.
Setting up to use S/MIME encryption
1. Get a certificate.
2. The first step to use S/MIME is to obtain a certificate, also called a digital ID, from your organization’s administrator. Your certificate may be stored on a smart card or may be a file that you store on your computer. Follow the instructions provided by your administrator to use your certificate.
3. Install the S/MIME control.
If you do not have the S/MIME control installed, and receive an encrypted or digitally signed message, you’ll be prompted to install the control when you open the message.
Alternatively, if you do not have the S/MIME control installed, you can create a new message and select more options  > Message options and select Encrypt this message (S/MIME). You will then be prompted to install the S/MIME control.
> Message options and select Encrypt this message (S/MIME). You will then be prompted to install the S/MIME control.
4. When you’re prompted to run or save the file, select Run.
You may be prompted again to verify that you want to run the software.
5. Select Run to continue the installation.
Note: You will have to close and reopen Outlook Web App before you can use the S/MIME control.
How do I encrypt individual messages
To add or remove digital encryption from an individual message that you’re composing:
1. Go to the top of the message and select more options  > Message options.
> Message options.
2. Select or deselect Encrypt this message (S/MIME).
If you encrypt an outgoing message and Outlook Web App can’t verify that all recipients can decrypt the message, you’ll see a notice warning you which recipients may not be able to read the encrypted message. You can then send the message anyway, remove those recipients, or retry to check again.
How do I digitally sign individual messages
To add or remove a digital signature from a message that you’re composing:
1. Click NEW MESSAGE Blue Button on left side of toolbar
 New Message
New Message
2. Go to the top of the message and on the toolbar, click ENCRYPT
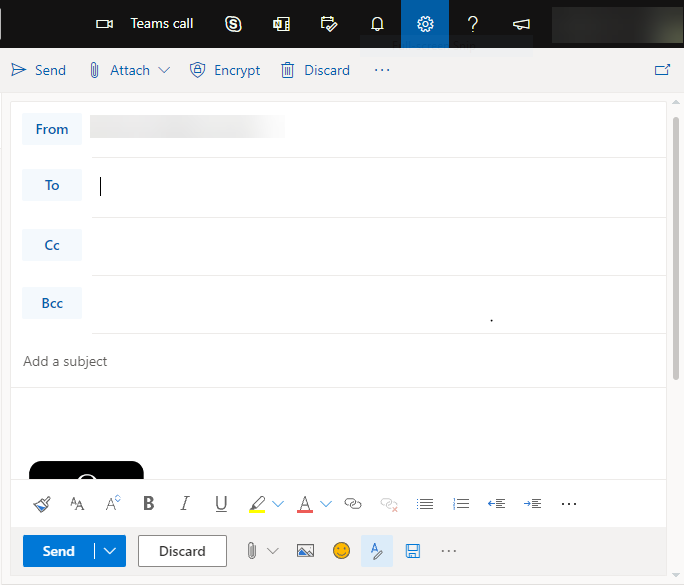 Encrypt
Encrypt
3. You will then see a menu that provides the choice to click ENCRYPT
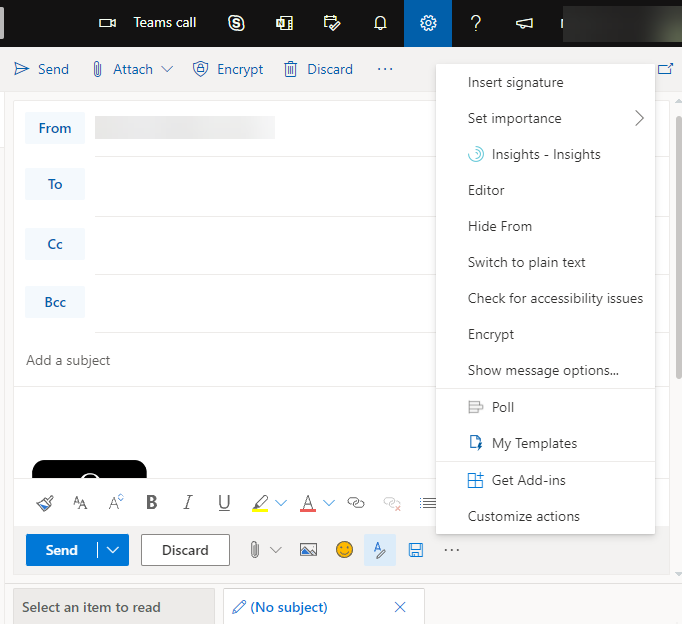 Encrypt
Encrypt
4. You can also click on the bottom right side of the new message, select the three dots (more options)  > Message options.
> Message options.
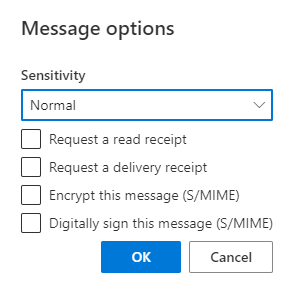 Message Options
Message Options
This option will allow you to encrypt the message using S/MIME.
5. You will then see a legend in the message telling you that the message is encrypted and you will see options presented in the message
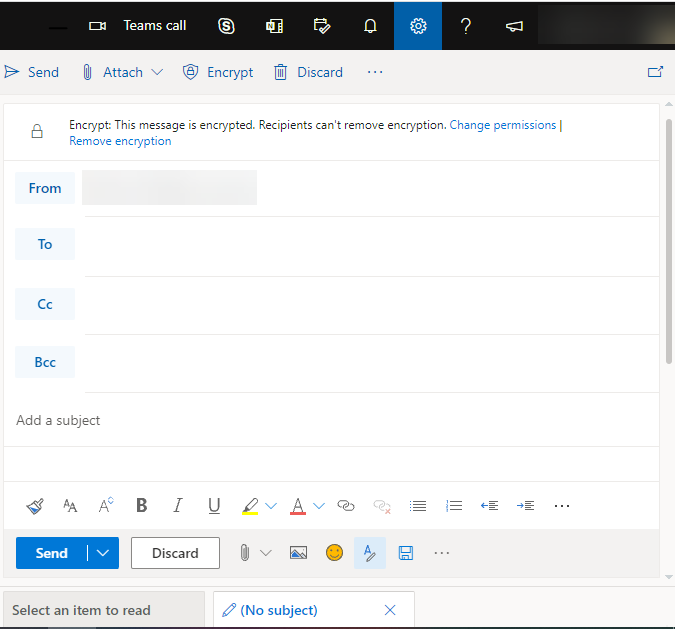 Message
Message
6. You can either click REMOVE ENCRYPTION, which will change your email display to a normal view or you can click on CHANGE PERMISSIONS, which will be displayed as follows:
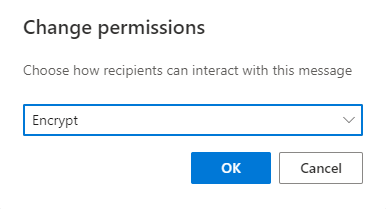 Change Permissions
Change Permissions
7. You can also select or deselect Digitally sign this message (S/MIME).
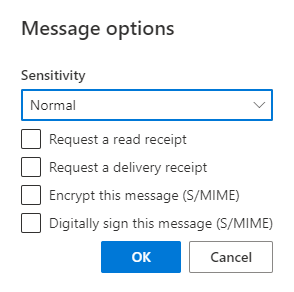 Message Options
Message Options
8. If your certificate is stored on a smartcard, you will be prompted to insert the smartcard to digitally sign the message. Your smartcard may also require a PIN to access the certificate.
Reading encrypted and digitally signed messages
How do I read an encrypted message?
1. A key icon  in the message list or reading pane indicates an encrypted message.
in the message list or reading pane indicates an encrypted message.
2. If you normally use Conversation View, you will have to open the message in a new window to read it. There will be a link on the message to make this easier.
3. When you receive an encrypted message, Outlook Web App will check whether the S/MIME control is installed and whether there is a certificate available on your computer.
If the S/MIME control is installed and there is a certificate available, the message will be decrypted when you open it.
If your certificate is stored on a smartcard, you will be prompted to insert the smartcard to read the message.
Your smartcard may also require a PIN to access the certificate.
How do I verify the signature of a digitally signed message
1. A ribbon icon  in the message list or reading pane indicates a digitally signed message.
in the message list or reading pane indicates a digitally signed message.
2. If you normally use Conversation view, you will have to open the message in a new window to read it. Information about the digital signature will be at the top of the message, along with a link that you can select to learn more about the digital signature.
How do I encrypt or digitally sign all messages
1. After you’ve installed the S/MIME control, you can go to the gear menu  > S/MIME settings where you will find two options that you can select to digitally encrypt or digitally sign every message you send.
> S/MIME settings where you will find two options that you can select to digitally encrypt or digitally sign every message you send.
2. Select Encrypt contents and attachment of all messages I send to automatically encrypt all outgoing messages.
3. Select Add a digital signature to all messages I send to digitally sign all outgoing messages.
Note: All outgoing messages include new messages, replies, and forwards.
S/MIME Message Encryption
Internal Recipients with the Organization
S/MIME message encryption is supported only on messages sent to and from recipients in your organization’s address list.
If you send an encrypted message to someone outside your organization, they will not be able to decrypt and read the message.
S/MIME digital signatures are only fully supported for recipients inside your organization.
Recipients can only verify the digital signature if they’re using an email client that supports S/MIME and have installed the S/MIME control.
Outside Recipients
If you send a digitally signed message to a recipient outside your organization, they will be able to read the message.
Depending on the email client they’re using, they may or may not see and be able to verify the digital signature.
Encrypted messages can be read only by intended recipients who have a certificate.
If you try to send an encrypted message to a recipient who doesn't have a certificate, Outlook Web App will warn you that the recipient can’t decrypt S/MIME encrypted messages.
If at least one recipient of an encrypted message has a certificate, Outlook Web App will send the message to all recipients.
If none of the intended recipients has a certificate, Outlook Web App won't let you send the message in encrypted form.
A digitally signed message reassures the recipient that the message hasn't been tampered with and verifies the identity of the sender.
Digitally signed messages can be sent to anyone. However, the recipient must be using an email application that supports S/MIME and have installed the S/MIME control to verify the digital signature
Forwarding Attachments in an Encrypted Message
If the encrypted message has attachments that you want to forward, they will not be sent automatically. You must first save them to your computer, and then re-attach the attachments to your encrypted message prior to forwarding.